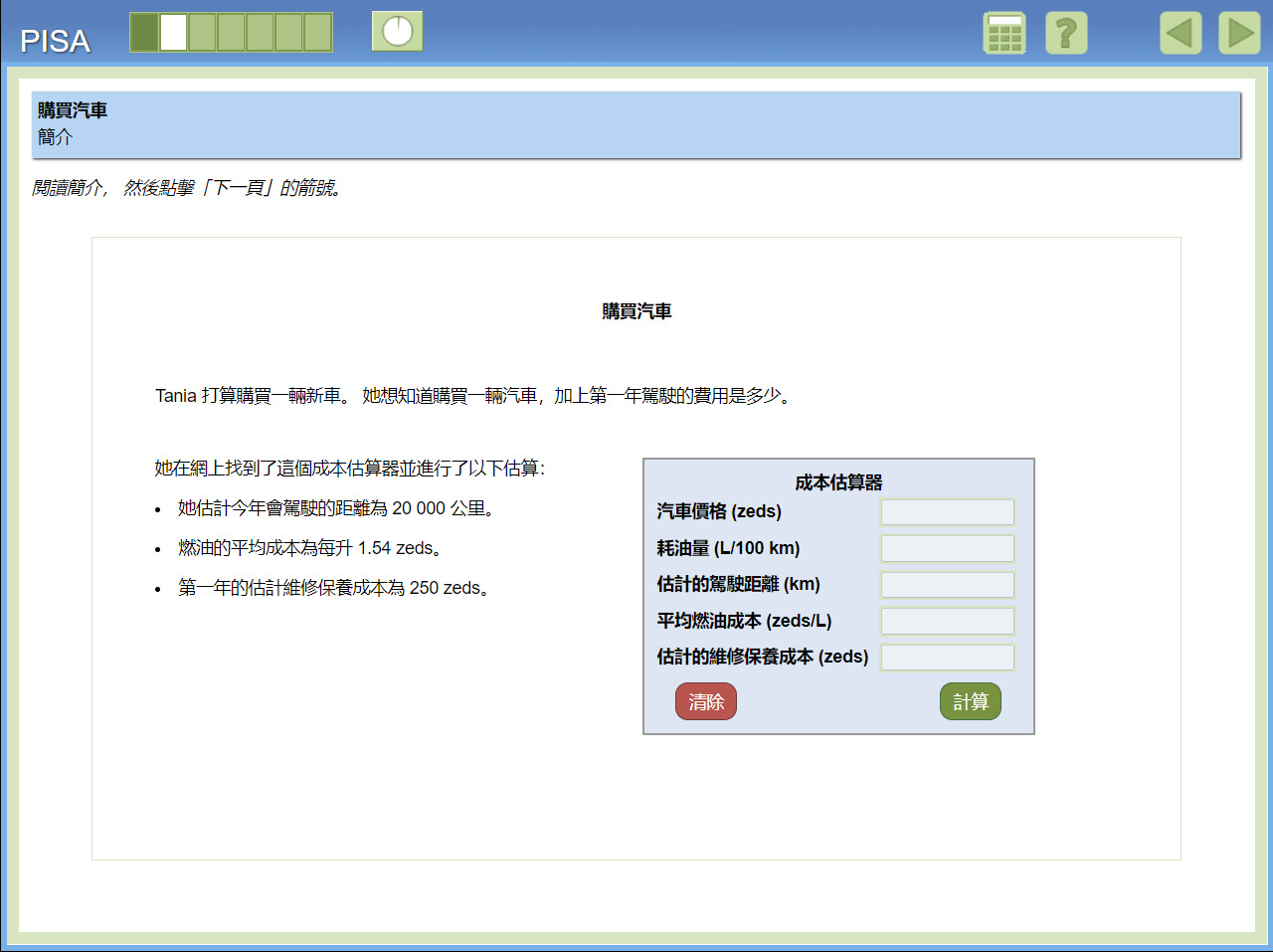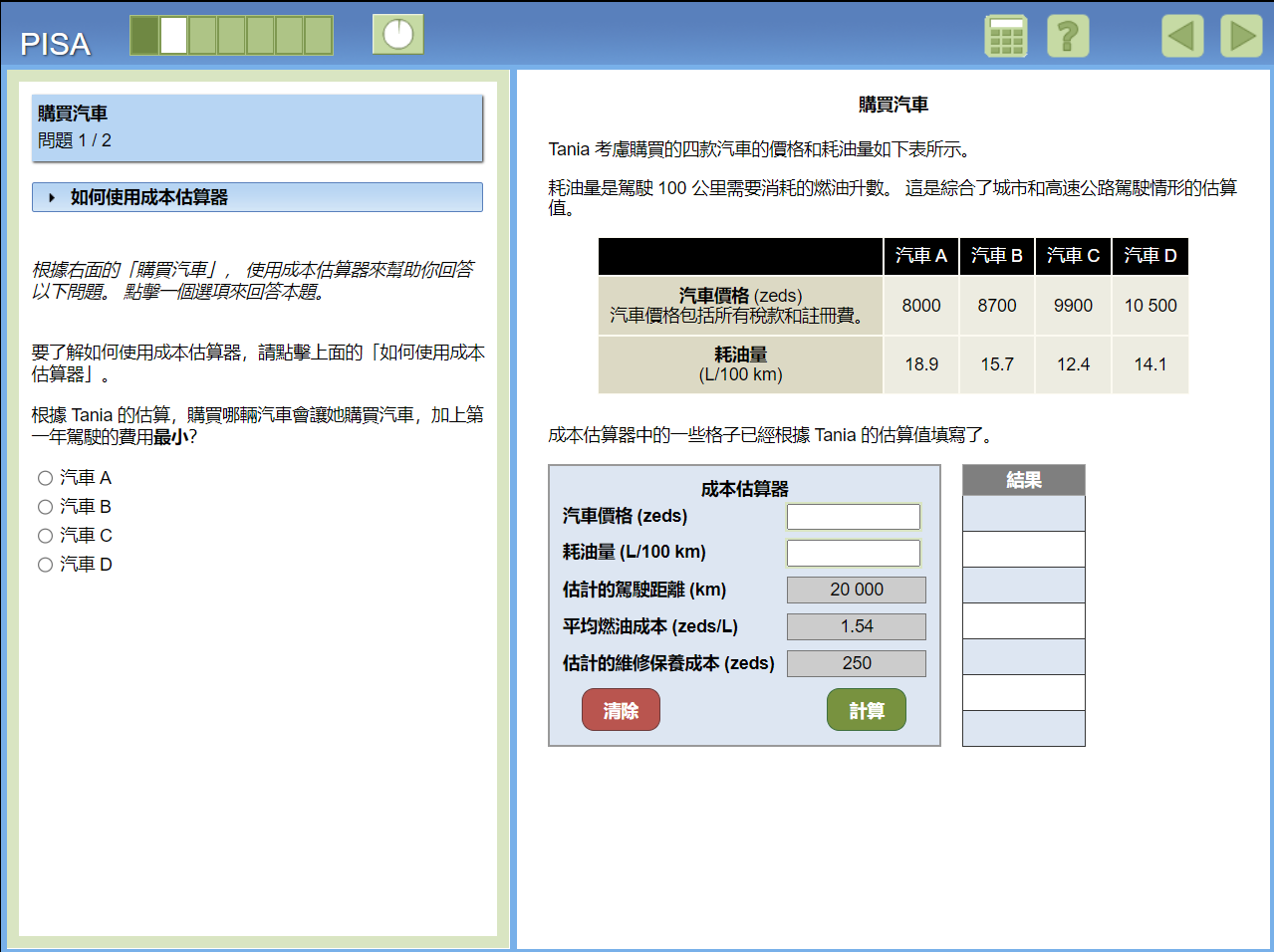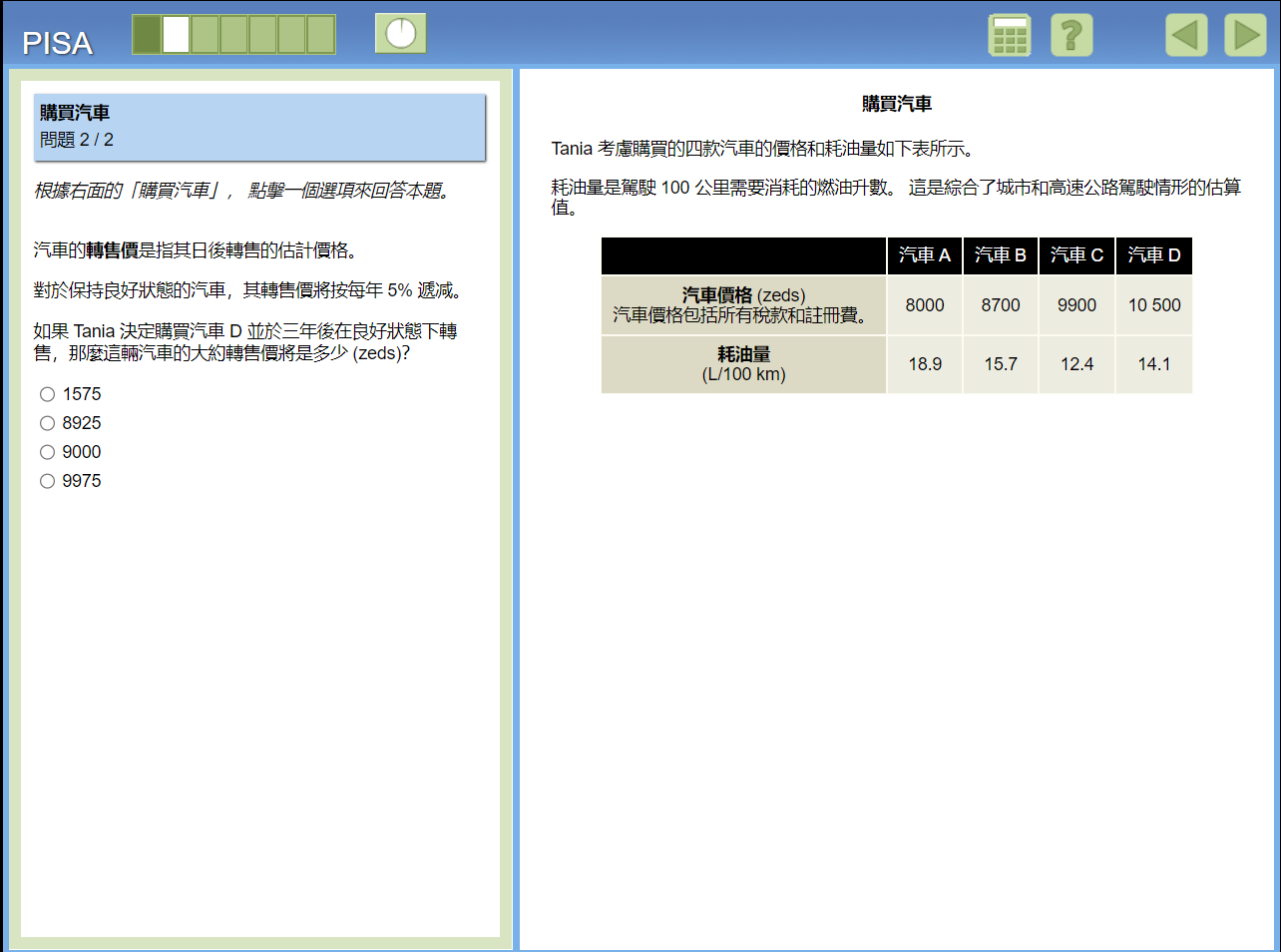
Mathematical Literacy
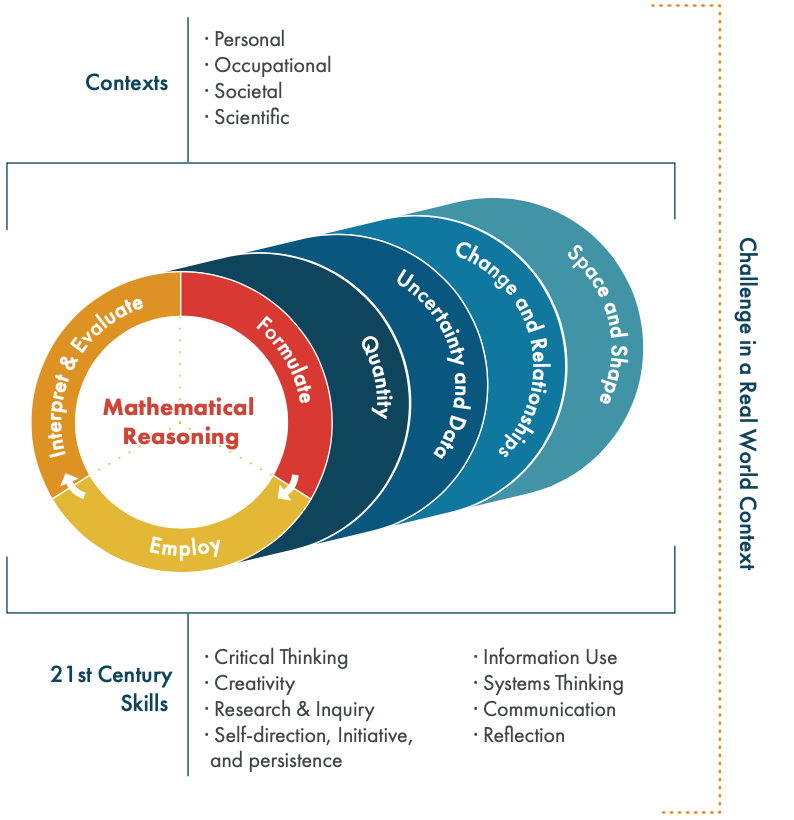
Mathematical literacy is an individual’s capacity to reason mathematically and to formulate, employ, and interpret mathematics to solve problems in a variety of real-world contexts. It includes concepts, procedures, facts, and tools to describe, explain, and predict phenomena. It helps individuals know the role that mathematics plays in the world and make the well-founded judgements and decisions needed by constructive, engaged and reflective 21st century citizens.
The PISA 2022 Mathematics framework (OECD) defines the theoretical underpinnings of the PISA mathematics assessment based on the fundamental concept of mathematical literacy, relating mathematical reasoning and three processes of the problem-solving (mathematical modelling) cycle. The framework describes how mathematical content knowledge is organised into four content categories: Change and relationships; Space and shape; Quantity; Uncertainty and data. Four categories of contexts in which students will face mathematical challenges are: personal; occupational; societal; and scientific.